Increasing Demands on PC Storage Due to Windows Memory Management

Increasing Demands on PC Storage Due to Windows Memory Management
Key Takeaways
- Windows Recall consumes up to 150 GB storage and requires at least 25 GB allocation.
- Copilot+ PCs have bulkier operating systems due to AI features, reducing usable storage space.
- Storage allocation for Recall determines the number of snapshots and the recallable history, with 10 GB providing around 35 hours of Recall.
Windows Recall comes at a cost—and it’s measured in gigabytes! As Copilot+ PCs hit the market, users may face a storage crunch, with the feature consuming up to 150 GB. But, practically speaking, how much space will you actually lose if you enable Recall to navigate your digital past?
What Is Windows Recall?
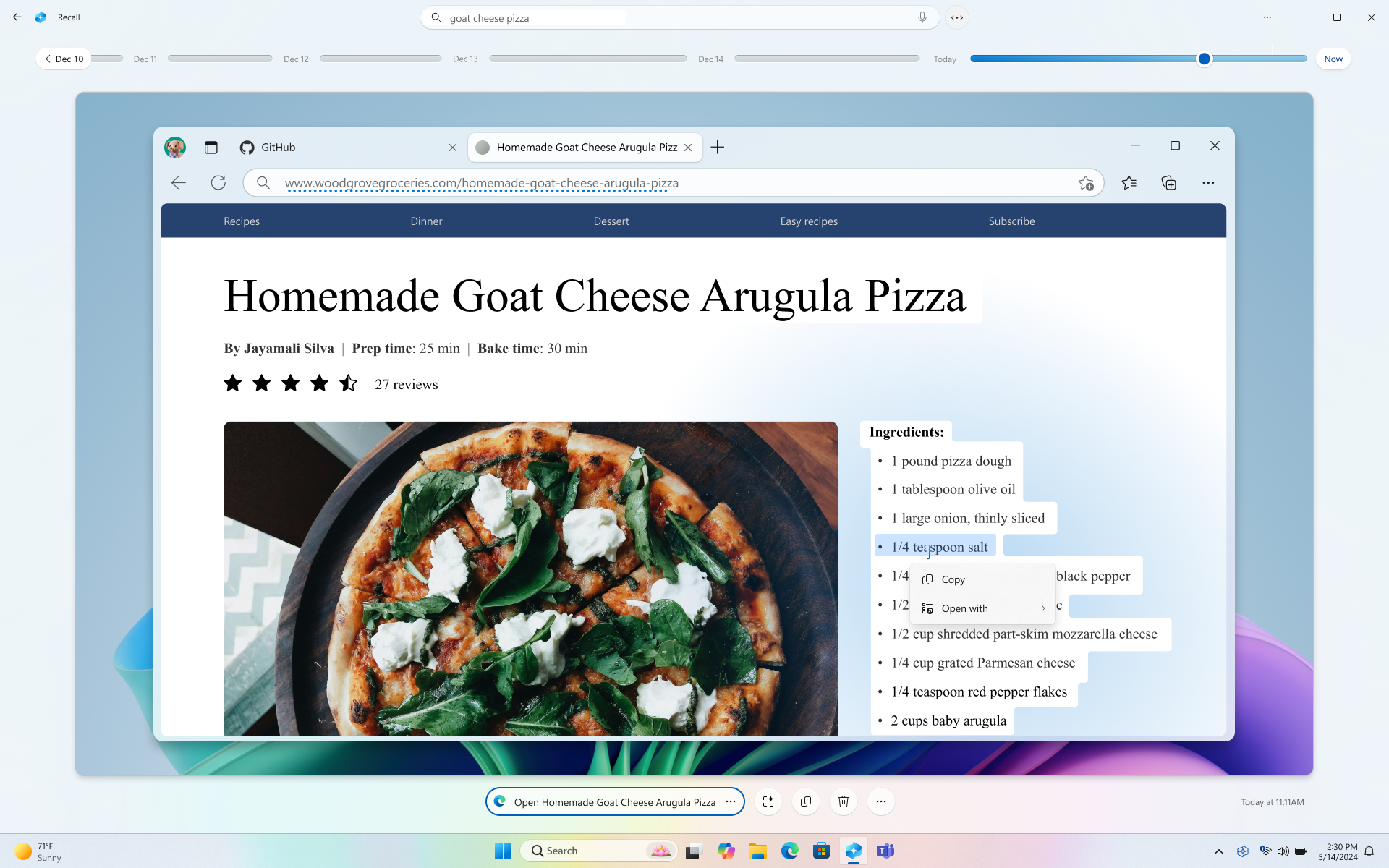
Microsoft is releasing a new line of AI-powered laptops called Copilot+ PCs and one of its features is called Windows Recall . It automatically captures snapshots of your screen activity, and then allows you to find or “recall” what you were doing using AI. For example, you can search for “Goat Cheese Pizza” and Recall will contextually scan through all the snapshots and showcase the website or app where there were instances matching your search query.
Windows Recall: An Overview of Storage Requirements
Here are the minimum system requirements for running Windows Recall:
- A Copilot+ PC
- 16 GB RAM
- 8 Logical Processors
- 256 GB Storage Capacity
- 50 GB Free Storage Space
- Windows Recall will stop taking screenshots when the free storage space is less than 25 GB.
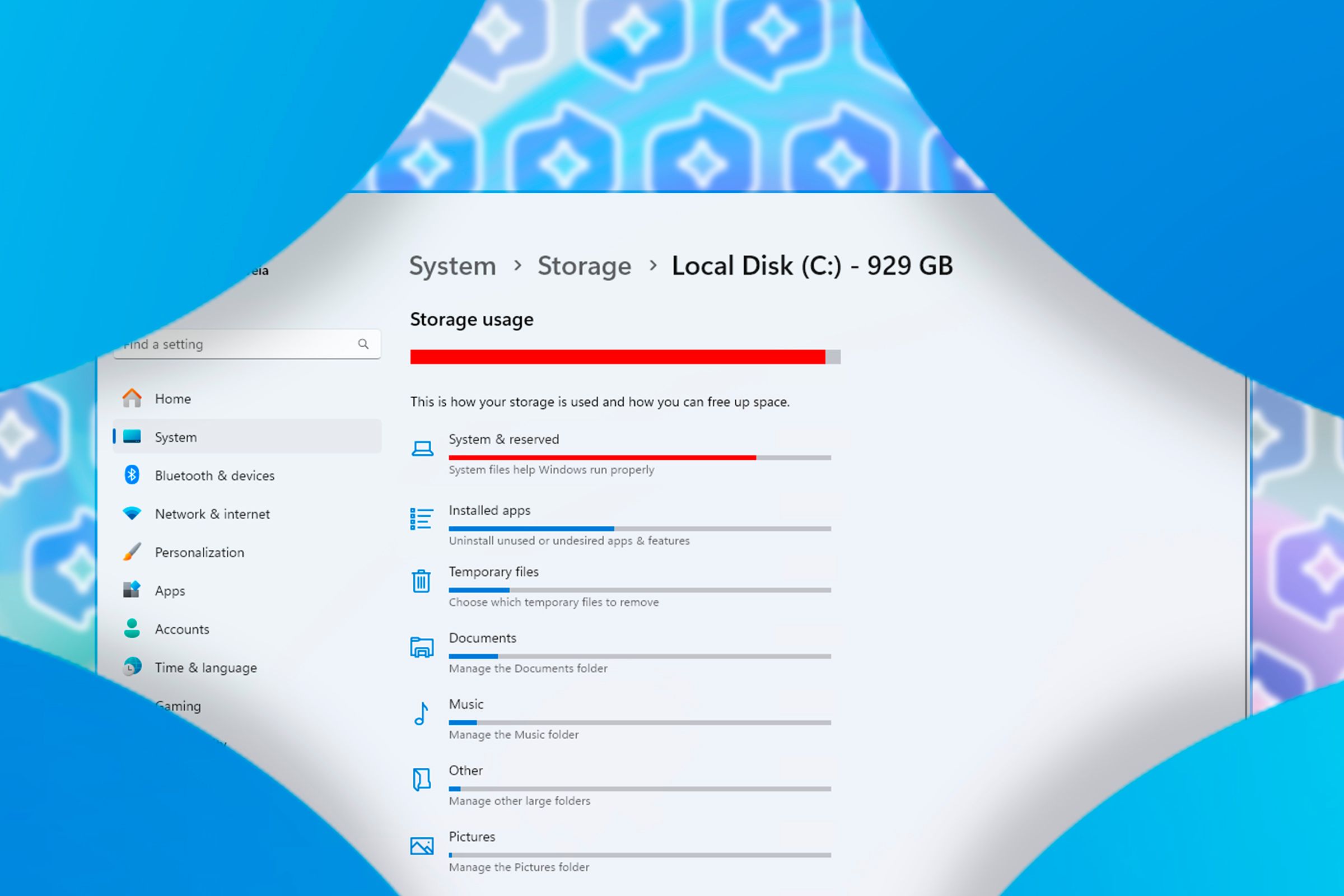
Also, the total amount of space you can allocate to Recall will vary depending on the total storage of your system.
- 256 GB devices: 25 GB (default) or 10 GB to Recall.
- 512 GB devices: 75 GB (default), 50 GB, or 25 GB to Recall.
- Devices with 1 TB or more: 150 GB (default), 100 GB, 75 GB, 50 GB, or 25 GB to Recall.
So, you need to allocate at least 25 GB to Recall if you wish to enable the feature—unless you own a 256 GB device, in which case, you can allocate just 10 GB. But wait, this is just the storage allocation for the snapshots—you’re actually losing a few more gigabytes to the systems powering Recall.
The True Weight of Windows Recall on System Storage
Windows Recall isn’t just about allocating space for the automatic snapshots. It also uses locally installed AI to analyze the snapshots and create a timeline of your activity. This means even if you disable Recall and don’t allocate any storage to it, you’ll still lose a chunk of your storage to the local AI, including the Recall app.
Usable Storage Space on Recall-Compatible Copilot+ PCs
On a 512 GB Copilot+ PC, you get 474 GB of available storage (which is standard) out of which 30 GB is allocated to the operating system and 14 GB to the system files.
Close
For reference, on regular Windows 11 PCs (non-Copilot+), the OS takes up just 17 GB, out of which only 6.21 GB of space goes to the system files.
Close
So, if you’re buying a Copilot+ PC, note that the operating system is going to be bulkier as it needs to allocate space for all the new AI features, including Recall. Also, if you intend to use the feature, you’ll need to allocate anywhere between 10-150 GB for storing the snapshots.
The total amount of space you allocate will determine how many snapshots you can store, equating to how far back you can “recall.” I personally doubt that 10 GB of storage allocation will give you a meaningful amount of Recall history. Practically, I think people will want to have access to at least 30 days of activity. So I ran the numbers, and you’d be surprised at just how much space the snapshots can eat up.
How Much Storage for 1 Hour of Recall
A single snapshot at 1080p resolution came out to 475 KB on my system. Of course, all the snapshots won’t be the same size but, on average, we can assume it to take up around 400 KB.
At the time of writing, Recall is on hold , and we don’t have the exact figures for how much storage the snapshots are taking up. Unless Microsoft is using a completely different image format or snapshot tool–which is unlikely—we can assume the same picture quality and file size as we get with the native Windows 11 snipping tool .
Now, Recall takes one snapshot every five seconds. This means it takes 12 snapshots a minute. So, every minute, Recall will store 400 KB x 12 = 4800 KB = 4.7 MB of snapshots, whereas every hour of Recall equals 4.7 MB x 60 = 282 MB of storage. That’s a lot!
In terms of storage allocation, this is how many hours of Recall you can expect:
- 10 GB storage allocation = ~35 hours of Recall
- 25 GB storage allocation = ~88 hours of Recall
- 50 GB storage allocation = ~177 hours of Recall
- 75 GB storage allocation = ~265 hours of Recall
- 100 GB storage allocation = ~354 hours of Recall
- 150 GB storage allocation = ~532 hours of Recall
So, if you use your PC for 12 hours per day (8 hours for work + 4 hours for personal stuff) and have allocated 25 GB storage to Recall, you can back up a week’s worth of usage history. However, you’ll need a 100 GB storage allocation to get a complete month of Recall.
Of course, the real number will vary depending on how much you use your PC, but this should give you an idea of what you can expect from Recall, depending on the storage allocation.
Recall only saves a snapshot if the content on the screen is different from the previous snapshot. So it won’t bulk up your storage when you aren’t using your PC or if you’ve paused the feature. You can also stop Recall from taking snapshots by following this guide .
So, How Much Storage Do You Have For Yourself?
A 256 GB SSD usually has 238 GB of available space , whereas a 512 GB SSD has 476 GB.
Now, if you buy a 256 GB Copilot+ PC, the system and preinstalled apps will eat up ~30 GB—more so if you enable Recall. Meanwhile, with a 512 GB model, you have the same ~30 GB for the system, along with a 25 GB minimum to Recall.
But that’s not all! The Copilot+ PCs will ship with SSDs, and you can’t max out the storage capacity . Ideally, you should leave ~10% of your SSD’s total capacity empty, or it’ll start slowing down and potentially lower the drive’s health and longevity.
This means that on a Recall-enabled 256 GB and a 512 GB Copilot + PC, you’ll have:
| | 256 GB Copilot+ PC | 512 GB Copilot+ PC | |
| ———————————————- | —————— | ———- |
| Available Storage | 238 GB | 476 GB |
| Storage Allocation for System & Reserved Files | 30 GB | 30 GB |
| Minimum Allocation to Recall | 10 GB | 25 GB |
| Keep Free for SSD Health | 25 GB | 47 GB |
| User Available Storage Space | 173 GB | 374 GB |
Considering these numbers and how large modern apps are getting, a 256 GB Copilot+ PC is just impractical and a 512 GB model debatable—only recommended if you don’t run heavy apps or play games.
Should You Buy a Higher Storage Model of a Copilot+ PC?
There’s no definitive answer, as it largely depends on your specific needs and the pricing structure. In some cases, you might find the price difference between a 256GB and a 512GB model is only $50, making the upgrade a no-brainer. However, when you’re looking at a $200-250 jump from 512GB to 1TB, the decision becomes less clear-cut.
When faced with this choice, consider two key factors—does the model support storage expansion, and what’s the price difference between storage variants? If the PC doesn’t allow storage expansion, get as much built-in storage as you think you’ll need.
On the other hand, if expansion is possible, compare the cost difference between variants to the price of third-party storage upgrades. Often, it’s more economical to purchase a lower-capacity model and expand the storage yourself later.
Also read:
- [New] How to Turn Video Soundtracks Into Audible Files for 2024
- [New] In 2024, Fast-Track To 1,000 Fans Through Captivating Content
- [New] In 2024, Getting Started with Stylish Mac-Made YouTube Vids
- [New] In 2024, How to Block YouTube Ads on Chrome/Firefox/Android/iPhone
- [New] In 2024, Intellect's Ultimate Guide to Premium GK Quiz Sites
- [Updated] How to Monetize Your YouTube Shorts Simple Steps for 2024
- [Updated] Single-Frame Solution Separate and Save Pics From Video in Windows Photos
- Best Pokemons for PVP Matches in Pokemon Go For Oppo A1 5G | Dr.fone
- How To Simulate GPS Movement With Location Spoofer On Vivo T2 Pro 5G? | Dr.fone
- In 2024, 3 Ways for Android Pokemon Go Spoofing On Motorola Moto G14 | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How to use Snapchat Location Spoofer to Protect Your Privacy On Vivo V27? | Dr.fone
- Solomon Speaks on Reconnecting Your Life | Free Book
- Steps for Retrieving Accidentally Formatted Partitions in Various Windows Versions
- Title: Increasing Demands on PC Storage Due to Windows Memory Management
- Author: Jeffrey
- Created at : 2024-11-16 18:31:23
- Updated at : 2024-11-19 17:42:56
- Link: https://eaxpv-info.techidaily.com/increasing-demands-on-pc-storage-due-to-windows-memory-management/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.